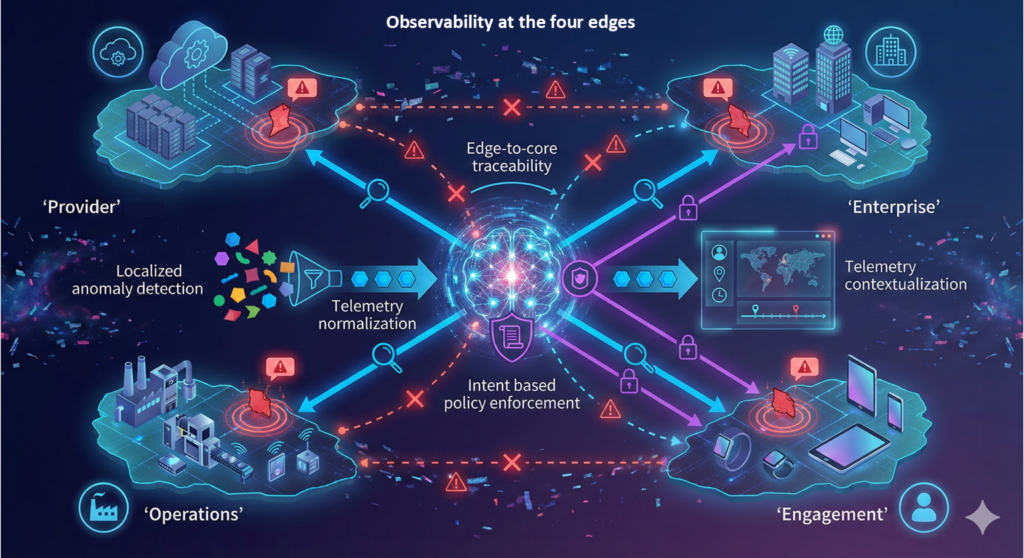
Technology stakeholders must recognize that observability insight needs to extend beyond monitoring IT systems to proactively detect, diagnose, and resolve issues impacting the health and performance of endpoint devices, processes, and systems. In the Forrester report The Strategic Role Of Observability At The Edge, we present different scenarios to demonstrate how insights can be derived from fragmented IT environments that have signals across mobile, IoT, and edge devices. They are transformed from isolated data points into a cohesive strategy across four edge environments.
The Scope Of Edge Scenarios Are Expanding Demand For Observability Insight
IT teams must correlate data from connected devices, sensors, AI models, APIs, and cloud services. These interconnected ecosystems depend on real-time visibility and observability insight. Each edge scenario involves distributed systems constantly generating telemetry across devices, platforms, and networks. Without observability, signals get lost, blind spots grow, and systems drift from intended outcomes.
Smart buildings are the new data centers for IT observability. Smart buildings generate telemetry from thousands of endpoints (e.g., HVAC units, lighting, environmental sensors). A room temperature spike might signal a failing sensor, a misconfigured automation rule, or a network delay. Observability platforms detect anomalies before the room becomes uncomfortable or equipment is compromised.
Every device endpoint should be monitored in the gig economy. Each remote worker has many endpoint devices (e.g., smartphones, tablets, AR/VR devices, wearables). Tech leaders need to track how apps and AI tools behave on devices in real-world conditions, and IT teams need visibility across the technology stack.
Edge telemetry must be trusted in logistics scenarios. Pharmaceuticals, luxury goods, and perishables rely on edge intelligence to track conditions, ensure compliance, and respond to supply chain disruptions. OT devices can generate video and environmental data that must be processed in real time to prevent accidents and meet compliance standards. Without observability, the signal can vanish in the storm.
Observability is the engine behind adaptive manufacturing intelligence. Heavy industry, such as shipbuilding, power generation, or aerospace manufacturing, runs on edge intelligence, where sensors, systems, and software work in sync across plants and regions. Observability is the control plane when production schedules shift daily, and IT teams must monitor telemetry across edge infrastructure, cloud, and AI models to keep operations smooth.
Edge, AI, and privacy collide in immersive retail environments. Virtual malls, AR-enhanced showrooms, and AI-personalized experiences are powered by edge devices and cloud services working in tandem. Insights must be extended across VR headsets and mobile apps to ensure fast response times or that sales are impacted. Localization requires observability across device types, languages, and regional standards.
Observability helps keep autonomous vehicle ecosystems safe. Autonomous vehicles are edge systems in motion. Every decision they make relies on real-time data from onboard sensors, external infrastructure, and cloud-based intelligence. Interoperability between personal devices, traffic systems, and back-end platforms is essential. Without observability, latency, packet loss, or misaligned models can make a smart vehicle blind — or deadly.
Schedule an inquiry or guidance session with Forrester analysts Carlos Casanova and Michele Pelino to hear examples of how observability at the edge enables enterprises to orchestrate global events, optimize manufacturing processes, power seamless customer experiences, and protect retail margins.